
Bad breath, or halitosis, is a common yet frustrating condition that many people struggle to eliminate. While poor oral hygiene, diet, and lifestyle habits are well-known contributors, the digestive system is often an overlooked source of chronic bad breath. Issues such as acid reflux, gut microbiome imbalances, intestinal permeability or leaky gut, and bacterial overgrowth can release foul-smelling gases that travel from the stomach to the mouth.
At Fresh Breath Center NYC, we take a holistic, science-backed approach to treating gut-related halitosis. By identifying underlying digestive issues and developing personalized treatment plans, we help patients achieve lasting fresh breath and improved overall health.
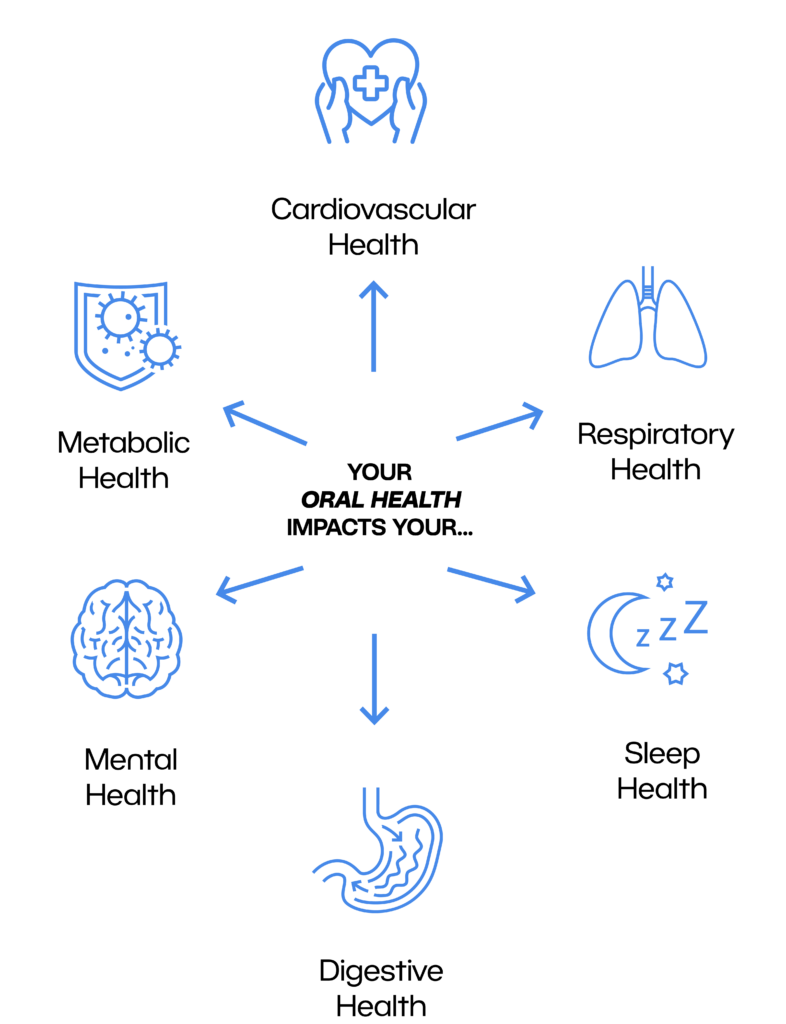
Bad breath isn’t always an oral issue—gut health plays a crucial role in maintaining fresh breath. When the digestive system is out of balance, gases and bacteria from the stomach and intestines can travel up the esophagus, causing chronic halitosis.
Several digestive disorders can lead to persistent bad breath, including:
A stomach ulcer, also known as a peptic ulcer, develops when stomach acid erodes the protective mucosal lining of the stomach, leading to an open sore. This can cause pain, discomfort, and, in some cases, chronic bad breath due to the release of sulfur compounds from the digestive system.
Symptoms of stomach ulcers can vary, but common signs include:
Stomach ulcers can develop for several reasons. The most common causes include:
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) occurs when stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, the tube that connects the stomach to the mouth. This acid reflux can cause discomfort, irritation, and, in many cases, chronic bad breath due to the presence of stomach acids and partially digested food particles in the mouth.
GERD can cause a range of uncomfortable symptoms, including:
A ring of muscle fibers known as the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) acts as a barrier between the stomach and esophagus, preventing stomach acid from rising into the throat and mouth. When the LES functions properly, acid remains in the stomach, aiding digestion. However, when the LES weakens or relaxes inappropriately, stomach acid flows back up into the esophagus, leading to irritation, inflammation, and GERD symptoms.
Several lifestyle and health factors can worsen GERD symptoms and increase the likelihood of acid reflux, including:
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a chronic digestive disorder that affects how the intestines function, leading to disruptions in bowel habits and gut health. Unlike structural conditions, IBS does not cause visible damage to the gastrointestinal tract but can significantly impact digestion and overall well-being.
There are four types of IBS:
While the exact cause of IBS remains unclear, research suggests that multiple systems in the body contribute to its development. Common triggers include:
IBS symptoms vary depending on the subtype:
Leaky gut, or intestinal permeability, occurs when the lining of the intestines becomes damaged, allowing bacteria, toxins, and undigested food particles to enter the bloodstream. This can lead to chronic inflammation, immune system imbalances, and a range of digestive and systemic health issues—including bad breath.
Leaky gut can affect more than just digestion. Common symptoms include:
While conditions like celiac disease and Crohn’s disease are known to contribute to leaky gut, many people develop intestinal permeability due to environmental and lifestyle factors such as:
When the intestinal barrier is compromised, it can trigger widespread inflammation and immune responses that extend beyond the digestive system, potentially leading to systemic health problems and chronic halitosis.
Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO) occurs when an excessive number of bacteria—normally found in the large intestine—begin to grow in the small intestine. This bacterial imbalance can interfere with digestion, cause fermentation of food, and lead to the release of foul-smelling gases that can be exhaled through the breath, resulting in chronic halitosis.
SIBO can cause a range of digestive issues that may also contribute to bad breath. Common symptoms include:
SIBO can develop due to a variety of underlying factors, including:

At Fresh Breath Center NYC, we recognize that treating gut-related bad breath requires more than just temporary solutions. Since digestive imbalances can play a major role in chronic halitosis, we take a multidisciplinary approach that goes beyond traditional dentistry.
Our team works closely with gastroenterologists, nutritionists, and functional medicine specialists to develop personalized treatment plans that address both oral and gut health. By targeting the root cause of halitosis, we not only improve breath freshness but also promote long-term digestive and overall well-being.
Our approach consists of several critical steps in order to understand the root cause of halitosis.
At Fresh Breath Center NYC, we are committed to providing comprehensive, patient-centered care that goes beyond temporary solutions. Our expert team is dedicated to identifying and treating the root cause of gut-related bad breath through advanced diagnostics, collaborative treatment plans, and cutting-edge technology.
We believe that bad breath should be treated holistically, not in isolation. That’s why we partner with leading experts in gastroenterology and nutrition to create personalized, science-backed treatment plans that address both oral and digestive health.
Your comfort and well-being matter to us. We take the time to listen to your concerns, answer your questions, and provide a supportive environment where you feel empowered throughout your treatment journey.
Our practice is equipped with state-of-the-art diagnostic tools that allow us to accurately identify the underlying causes of chronic halitosis. From oral and gut microbiome testing to advanced breath analysis, we use the latest scientific advancements to ensure effective, long-term results.
Bad breath caused by gut imbalances can be frustrating and difficult to manage on your own. At Fresh Breath Center NYC, we specialize in uncovering the root cause of chronic halitosis and creating personalized, science-backed treatment plans to restore fresh breath and overall digestive health.
Don’t let gut-related bad breath impact your confidence any longer. Schedule a consultation today to receive a comprehensive evaluation and customized treatment plan designed specifically for you.
Contact us now to start your journey toward lasting fresh breath and improved well-being.
Located in the heart of the community, we have built a reputation for excellence and trust, ensuring every visit to our practice is a positive and rewarding experience.
Monday | 9am – 5pm
Tuesday | 9am – 5pm
Wednesday | 9am – 5pm
Thursday | 9am – 5pm
Friday | 9am – 1pm
Saturday | Closed
Sunday | Closed
Monday | 9am – 5pm
Tuesday | 9am – 5pm
Wednesday | 9am – 5pm
Thursday | 9am – 5pm
Friday | 9am – 5pm
Saturday | Closed
Sunday | Closed